When 2 Billion+ NPM Downloads Get Hijacked: Anatomy of a Major Supply-Chain Attack

On September 8, 2025, a remarkably large-scale npm supply-chain attack was uncovered—one of the most severe in JavaScript’s history. A trusted maintainer’s npm account was compromised via phishing, enabling attackers to inject cryptostealer malware into 18 popular packages (e.g., chalk, debug, ansi-styles), collectively accounting for around 2.6 billion weekly downloads     .
The Attack: What Happened
1. Phishing Setup
A fraudulent email, sent from support@npmjs.help, a look-alike domain of the legitimate npm support, urged the maintainer known as Qix (Josh Junon) to update their 2FA, claiming their account would be locked on September 10. Despite caution, Junon clicked the link during a busy day and entered credentials on the fake site.

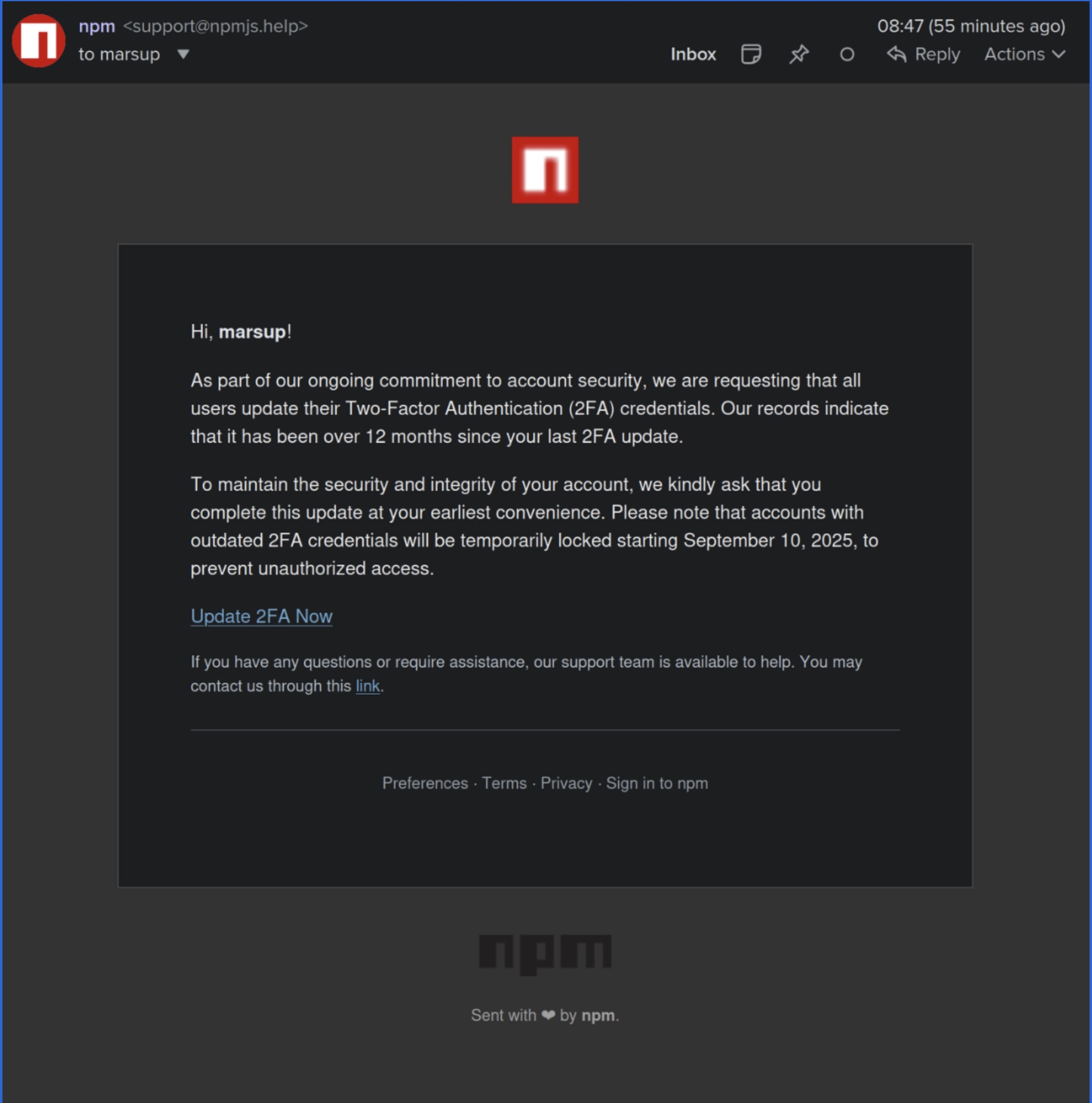
2. Compromise of Maintainer Account
The attackers then used the compromised credentials to push malicious versions of 18 packages, including chalk (~300 M weekly downloads), debug (~358 M), ansi-styles (~371 M), supports-color, strip-ansi, and more.


Largest NPM Compromise in History - Supply Chain Attack
by u/Advocatemack in programming

3. Rapid Detection & Containment
Aikido Security detected the compromise within five minutes, and it was publicly disclosed within about an hour, limiting further spread.


Malware Mechanics & Impact
The injected malware was tailored to target Web3 browser wallets. It intercepts wallet-related API calls, like window.ethereum, fetch, or XMLHttpRequest, and silently swaps destination addresses, redirecting crypto funds to attacker-controlled accounts. Ledger’s CTO Charles Guillemet warned that this could put billions of dollars in crypto assets at risk, although early estimates suggest only under $50 in actual crypto was stolen before mitigation began.

SOCRadar’s CISO called this event a “watershed moment” for software supply-chain security, highlighting how attackers exploited the foundational trust in open-source ecosystems—without having to breach infrastructure, they simply hijacked a trusted account.

Broader Implications
- Single Point of Failure in Open Source
This incident underscores how compromising just one maintainer can cascade through vast swathes of the ecosystem—a longstanding risk in npm, which heavily relies on a few high-impact maintainers.


- Growing Threat Surface with Web3 Integration
The attack’s focus on crypto wallet hijacking is emblematic of evolving targets—now that Web3 wallets run within browser contexts, supply-chain compromises have stealthy, high-stakes consequences.

- Need for Strategic Improvements
The speed of detection and response was outstanding—but it points to the need for better proactive defenses: least-privilege execution, permissioned package behavior, and enhanced vetting mechanisms.

Mitigation & Best Practices
Here’s a structured defensive playbook for publishers and developers:
Maintainers
- Use hardware-based 2FA (not just email or SMS)
- Verify sender domains carefully; don’t follow 2FA prompts via email
- Limit scope of maintainership, apply principle of least privilege
Developers / Consumers
- Pin dependency versions in
package.json&package-lock.json - Use npm audit and static scanning tools
- Conduct manual reviews of updates for critical packages
- Implement runtime sandboxing or permission-based models (e.g. restrictions on network or wallet APIs)

Registry / Ecosystem
- Introduce warning systems for anomalous update activity
- Enforce code signing for high-impact packages
- Offer optional “trusted maintainer” vetting
- Educate maintainers on phishing and impersonation tactics
⸻
Final Thoughts
While disconcerting, this incident also showcased the strength of the open-source community: rapid detection, transparent communication, and swift package rollback prevented far greater harm.
But it’s a clear wake-up call: trust alone isn’t enough. Supply-chain security must be reinforced through layered defenses—technical, procedural, and educational. If you’re building GenAI or cloud-based ecosystems (as I know you are!), investing in dependency hygiene and hardened deployment pipelines now will pay long-term dividends.














